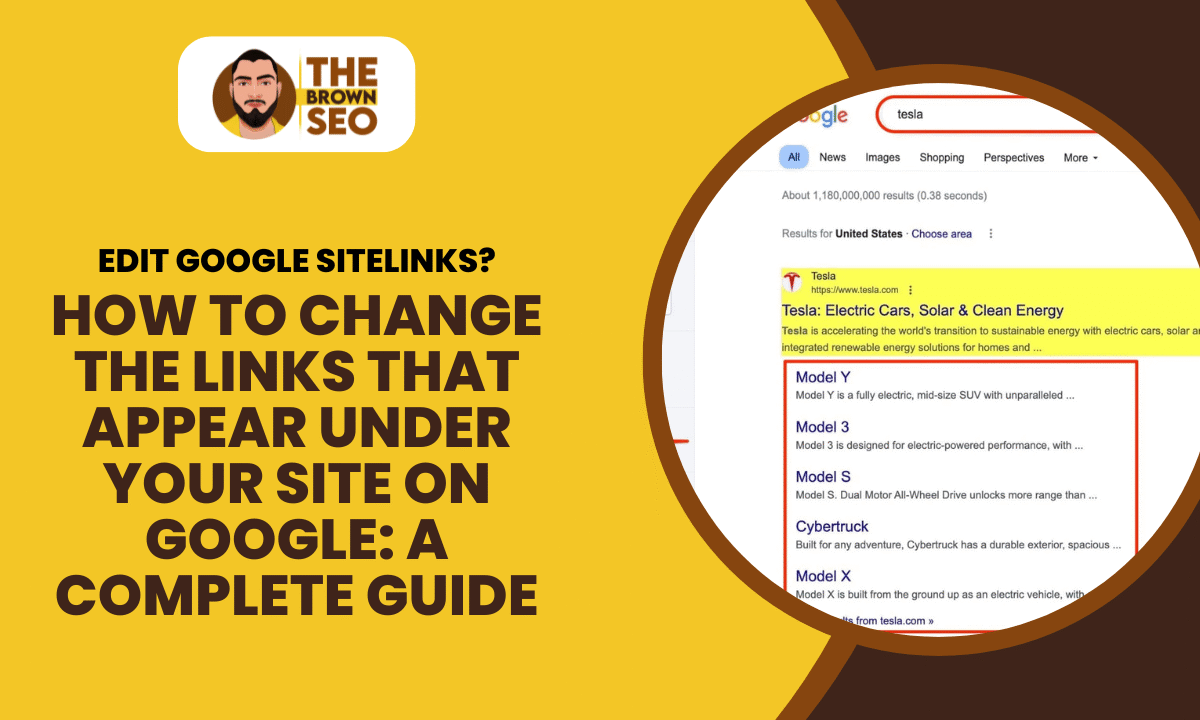
When you search for your website on Google, you may notice additional links appearing below your main search result. These are known as Google sitelinks. They help users navigate your site more efficiently. But what if you want to change, remove, or optimize these links?
This guide will walk you through how to change the links that appear under your site on Google, ensuring that your website displays the most relevant pages to visitors.
Understanding Google Sitelinks
Sitelinks are automatically generated by Google’s algorithm based on what it considers the most useful pages on your site. These links appear beneath your website’s main search result and are meant to enhance user experience by providing direct access to important pages.
There is no direct option to manually select or edit these sitelinks in Google Search Console or any other tool. However, by optimizing your website’s structure, content, and navigation, you can influence which pages appear as sitelinks and improve the way users engage with your site.
Why Are Google Sitelinks Important?
- Improve Click-Through Rates (CTR):Sitelinks provide direct shortcuts to key pages, increasing user engagement and CTR.
- Enhance User Experience:By offering quick access to essential sections, sitelinks make navigation easier for visitors.
- Boost SEO Performance:Well-structured sitelinks signal a strong site hierarchy, which can improve overall search rankings.
- Increase Brand Authority:A properly structured website with sitelinks appears more authoritative and credible in search results.
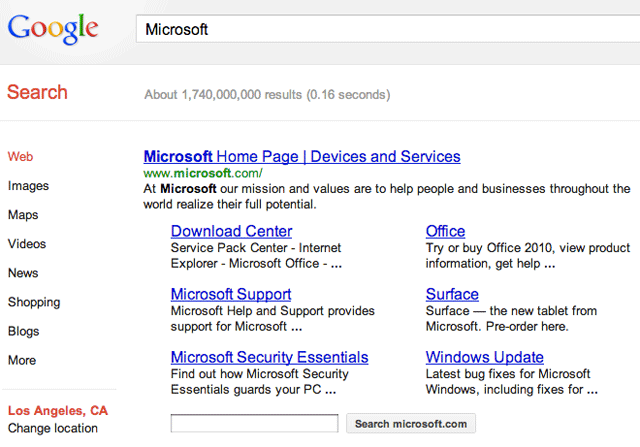
Step-by-Step Process to Change the Links That Appear Under Your Site on Google
1: Optimize Your Site Structure
Google prioritizes well-structured sites when selecting sitelinks. To improve your chances of getting desired sitelinks:
- Use a clear and logical navigation menu with properly categorized pages.
- Ensure that important pages are easily accessible from the homepage and do not require multiple clicks.
- Use a breadcrumb navigation to reinforce site hierarchy, helping Google understand relationships between different pages.
- Ensure that each page has a distinct and descriptive URL structure.
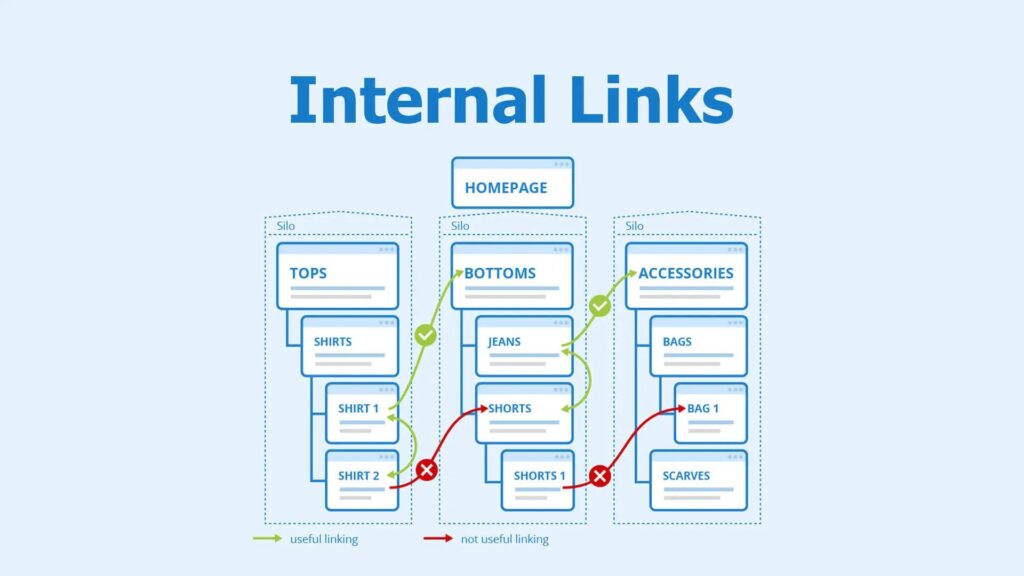
2: Use Internal Linking Strategically
Google scans your internal links to determine which pages are important. To guide it:
- Link important pages more frequently within your content.
- Use descriptive anchor text when linking to key pages instead of generic phrases like “click here.”
- Remove internal links pointing to less relevant pages that you don’t want appearing as sitelinks.
- Avoid excessive linking to pages that should not be featured prominently.
3: Optimize Your Meta Titles and Descriptions
Meta titles and descriptions play a crucial role in influencing how sitelinks appear. To optimize them:
- Write clear and compelling page titles that accurately describe the content and purpose of each page.
- Use concise and unique meta descriptions to ensure they align with search intent.
- Avoid duplicate or vague page titles that may confuse Google when selecting sitelinks.
- Use structured data markup to provide more context to search engines.

4: Remove Undesired Sitelinks Using Google Search Console
If unwanted links appear as sitelinks, you can try to de-emphasize them:
- Log into Google Search Console (https://search.google.com/search-console/).
- Navigate to Search Performance > Pages to identify underperforming pages.
- Remove internal links pointing to those pages.
- Add a noindex tag to less important pages if they do not need to be indexed.
- Consider adjusting your site’s structure to prevent less important pages from being featured prominently.
5: Submit a Sitemap with Prioritized URLs
A properly structured sitemap helps Google understand which pages are important and should be considered for sitelinks.
- Use tools like Yoast SEO (for WordPress) or XML Sitemaps Generator to create and manage your sitemap.
- Submit your sitemap via Google Search Console > Indexing > Sitemaps to ensure Google prioritizes the right pages.
- Prioritize key pages by ensuring they are well-linked, contain valuable content, and have proper metadata.
6: Increase Click-Through Rate (CTR) for Preferred Pages
Google favors pages with higher user engagement and click-through rates. To influence sitelinks:
- Improve page content for high-value pages by adding compelling headlines and relevant keywords.
- Use clear call-to-action (CTA) elements to increase user interaction.
- Optimize pages for faster loading speeds, mobile-friendliness, and responsive design.
- Conduct A/B testing to see which versions of pages perform best in search results.
7: Monitor and Adjust Regularly
Google updates sitelinks based on site changes, user behavior, and search trends. Regularly:
- Check Google Search Consoleto monitor sitelink changes and adjust your strategy accordingly.
- Analyze user behaviorusing Google Analytics to identify which pages receive the most traffic and engagement.
- Adjust your internal linking, page optimization, and metadatabased on performance insights.
- Regularly update your website to ensure relevant and high-quality content is maintained.
Final Thoughts
While you cannot manually choose sitelinks, you can significantly influence them by optimizing your site structure, internal linking, and meta information. By following these steps, you’ll have a better chance of displaying the most relevant links under your website on Google, improving navigation, user experience, and SEO rankings.
Start optimizing today and take control of how your website appears in search results!
