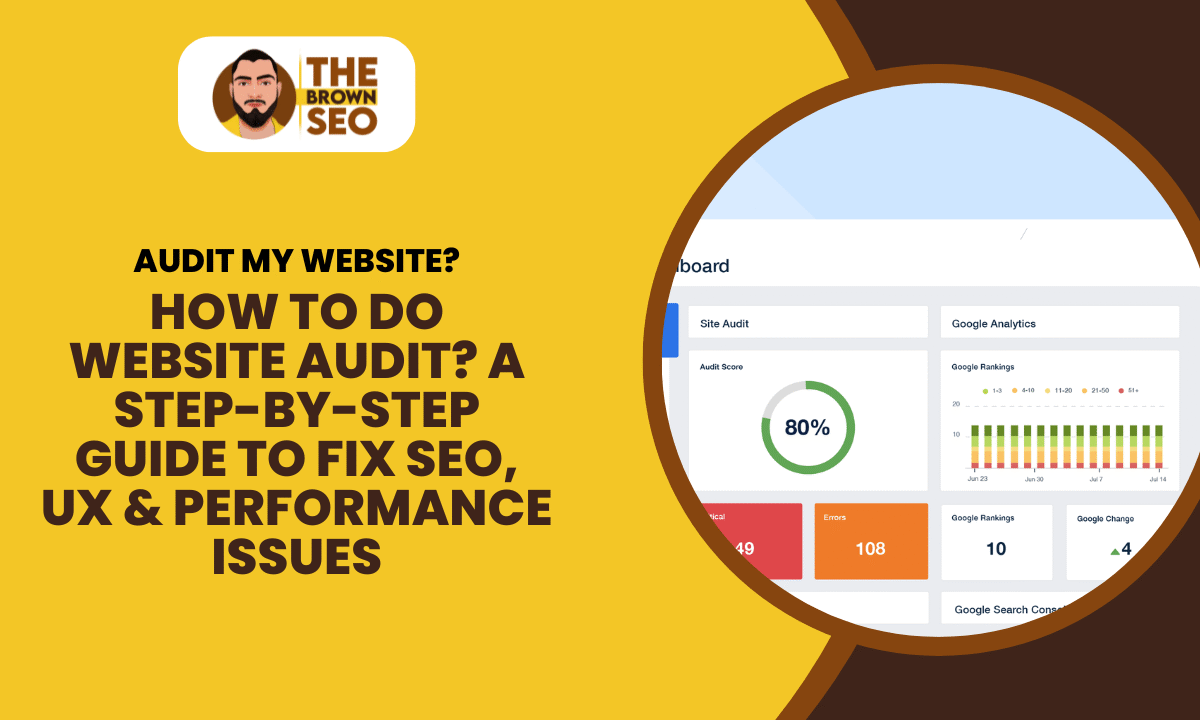
A website might look great on the surface, but under the hood, there could be hidden issues dragging down your traffic, SEO rankings, or user engagement. That’s where knowing how to do website audit becomes critical. Whether you’re an SEO expert, digital marketer, or business owner, auditing your website can reveal actionable insights that can make or break your online presence.
In this comprehensive guide, you’ll learn how to do website audit the right way—covering everything from technical performance to SEO, content, mobile usability, and more.
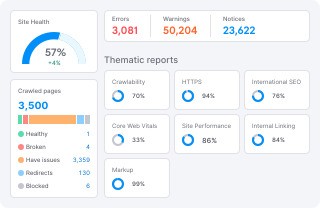
What Is a Website Audit and Why It Matters?
A website audit is a comprehensive evaluation of your website’s overall health. It analyzes multiple aspects like:
⦁ Technical SEO
⦁ On-page content
⦁ User experience (UX)
⦁ Page speed
⦁ Mobile responsiveness
⦁ Security issues
By learning how to do website audit, you can identify critical problems, boost search rankings, improve user engagement, and increase conversions.
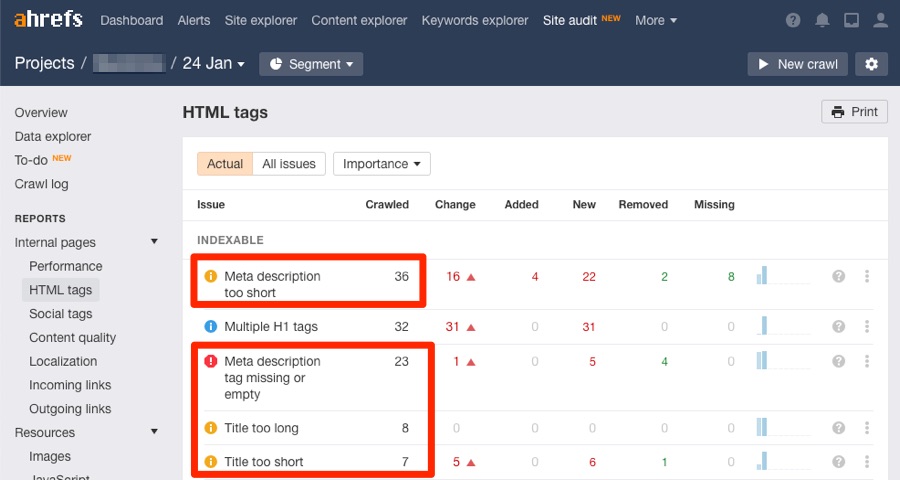
How to Do Website Audit: Step-by-Step Breakdown?
1. Start with a Crawl of Your Website
Use tools like:
⦁ Screaming Frog
⦁ Ahrefs Site Audit
⦁ SEMrush Site Audit
⦁ Sitebulb
A crawl will identify:
⦁ Broken links (404 errors)
⦁ Duplicate content
⦁ Redirect chains
⦁ Canonical issues
⦁ Meta tags and headings
Tip: Always crawl your full site to get a complete picture before fixing anything.
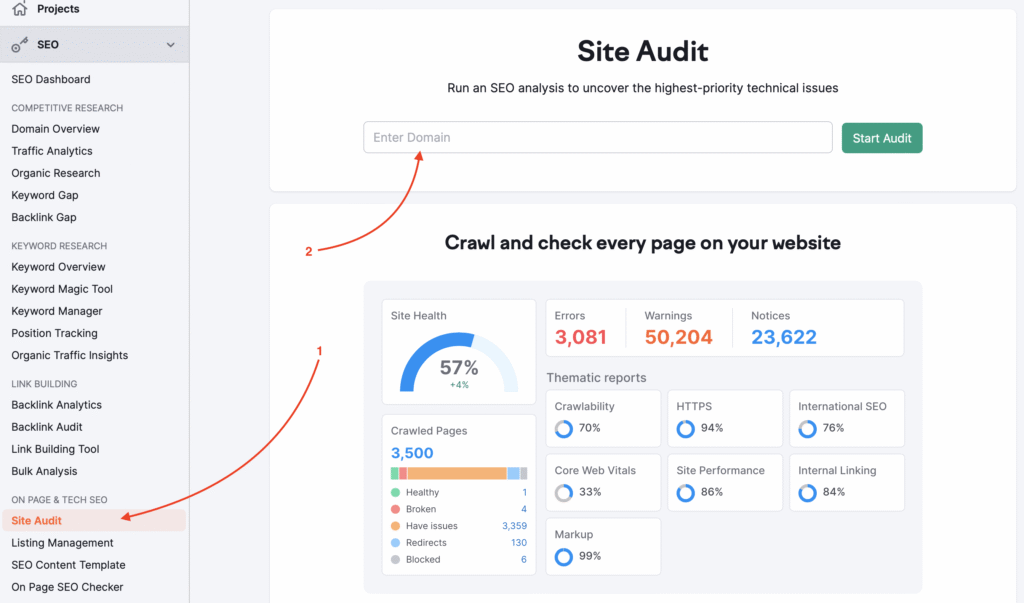
2. Check for Indexing & Crawlability
⦁ Use Google Search Console to ensure all critical pages are indexed.
⦁ Look for:
⦁ Pages excluded from indexing
⦁ Robots.txt disallow rules
⦁ Noindex meta tags
⦁ Check the sitemap submission and coverage errors.
Knowing how to do website audit means understanding what search engines can and can’t see on your site.
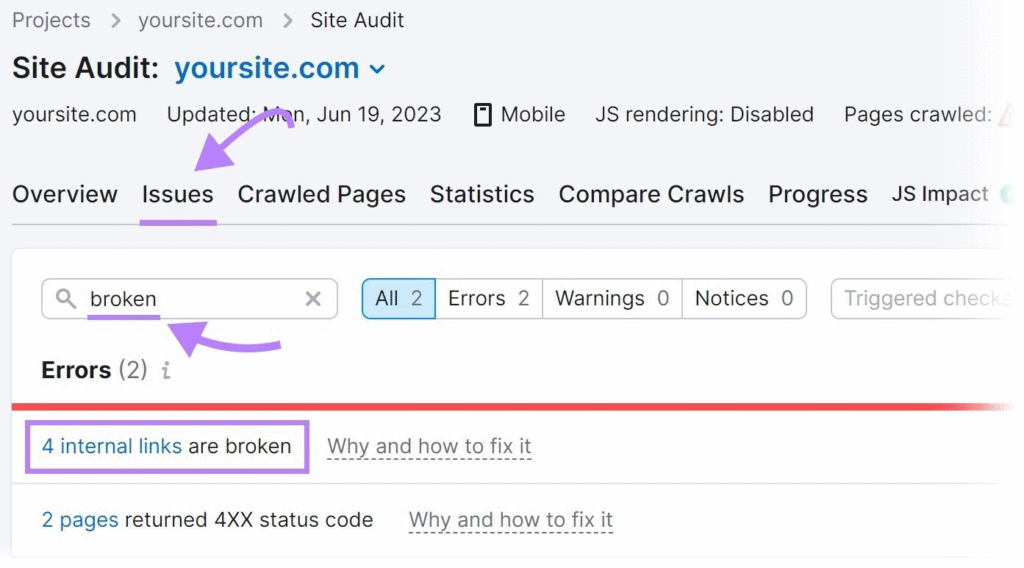
3. Audit On-Page SEO Elements
Review key on-page components:
⦁ Title tags: Unique, under 60 characters
⦁ Meta descriptions: Compelling, under 160 characters
⦁ Headings: Proper use of H1, H2, H3 hierarchy
⦁ Image alt texts: Descriptive and keyword-rich
⦁ Internal linking: Logical and crawlable
Use tools like Surfer SEO or Yoast SEO for on-page suggestions.
4. Analyze Site Speed & Performance
Use tools like:
⦁ Google PageSpeed Insights
⦁ GTmetrix
⦁ WebPageTest.org
Key metrics to review:
⦁ Largest Contentful Paint (LCP)
⦁ Time to First Byte (TTFB)
⦁ First Input Delay (FID)
⦁ Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS)
Tip: Compress images, use lazy loading, and reduce third-party scripts to improve performance.
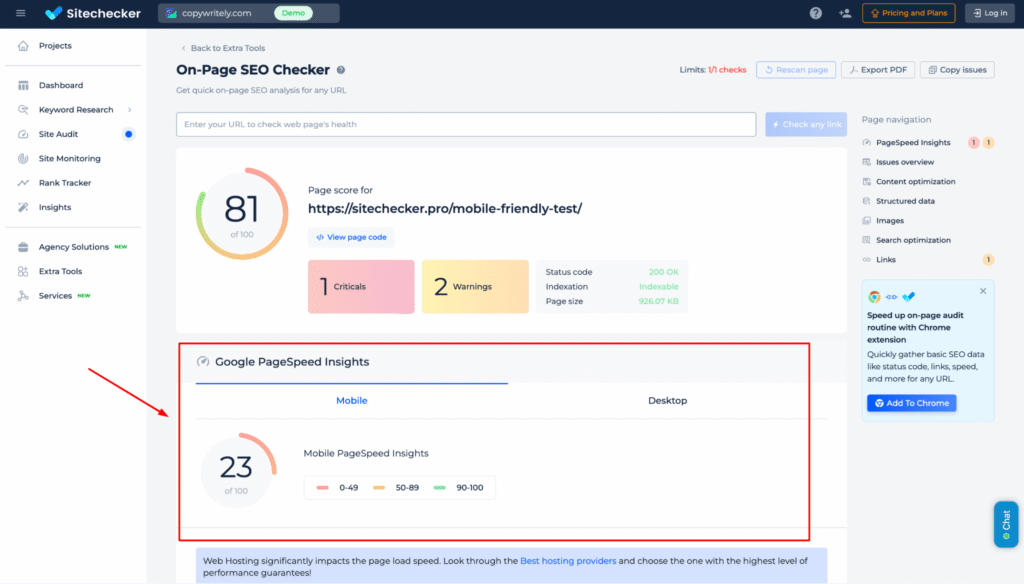
5. Check Mobile Friendliness
Use Google’s Mobile-Friendly Test and look for:
⦁ Responsive design
⦁ Clickable elements not too close
⦁ Readable text
⦁ Fast load time on mobile
More than 60% of traffic comes from mobile. When learning how to do website audit, you can’t ignore mobile UX.
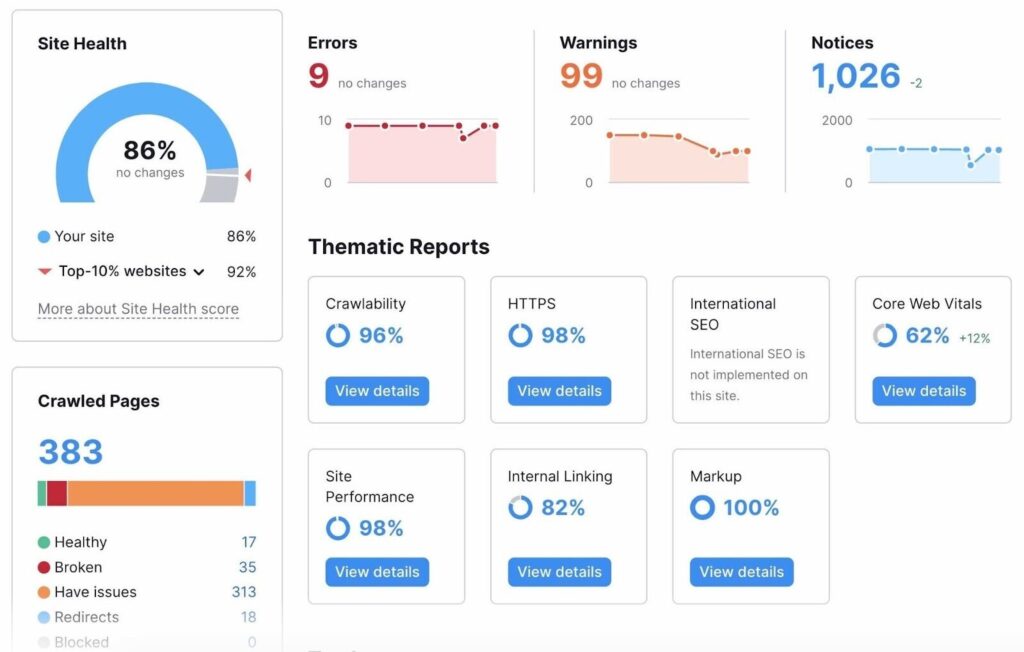
6. Inspect Technical SEO
Ensure your technical foundation is solid:
⦁ HTTPS enabled
⦁ Canonical tags correctly implemented
⦁ Structured data (Schema.org) markup
⦁ Pagination setup (rel=”prev” and rel=”next”)
⦁ URL structure: short, clean, keyword-rich
7. Evaluate Content Quality & Gaps
Run a content audit using:
⦁ Google Analytics (check bounce rate and dwell time)
⦁ Google Search Console (analyze impressions vs. clicks)
⦁ Ahrefs/SEMrush content gap tools
Look for:
⦁ Thin content (under 300 words)
⦁ Duplicate content
⦁ Outdated posts
⦁ Pages with no traffic or backlinks
This is a crucial part of how to do website audit for improving keyword relevance and topical authority.
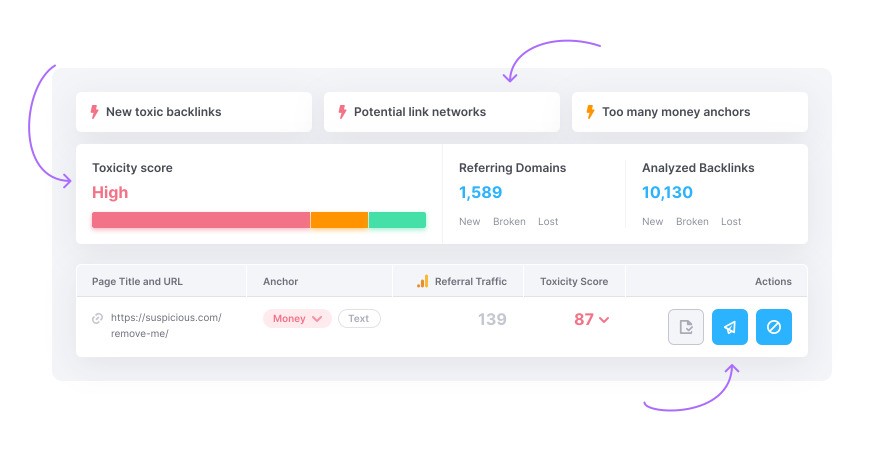
8. Review Backlink Profile
Use tools like:
⦁ Ahrefs
⦁ Moz
⦁ Majestic
Look at:
⦁ Total backlinks and referring domains
⦁ Toxic or spammy links
⦁ Lost and new links
⦁ Anchor text distribution
Disavow toxic backlinks if needed.
9. Test Site Security
Check for:
⦁ SSL certificate (HTTPS)
⦁ Vulnerable CMS/plugins
⦁ Outdated scripts
⦁ Open ports (use security scanners like Sucuri)
Security issues can hurt your rankings and user trust.
10. Generate a Website Audit Report
Once you’ve completed all steps, compile a detailed report covering:
⦁ Found issues
⦁ Suggested fixes
⦁ Priority levels (High/Medium/Low)
⦁ Visual screenshots or graphs for explanation
⦁ Action plan with timelines
This is essential for tracking progress and communicating with stakeholders.
Bonus Tools to Help You Do a Website Audit Efficiently
Tool Purpose
Google Search Console Indexing, performance, mobile usability
Google Analytics Traffic sources, bounce rate, behavior flow
Screaming Frog In-depth crawling and technical SEO
Ahrefs / SEMrush Backlink and keyword analysis
GTmetrix Speed and performance
Siteliner Duplicate content
Surfer SEO On-page SEO optimization
SEOquake Quick on-page audits (browser extension)
Conclusion
Knowing how to do website audit isn’t just a technical checklist—it’s a strategic process that identifies what’s holding your site back from ranking and converting. Regular audits reveal hidden issues before they become major problems, making them a core part of any long-term SEO or digital growth strategy.
If you want your website to stay healthy, competitive, and aligned with the latest Google updates, learning how to do website audit is not optional—it’s mandatory.
